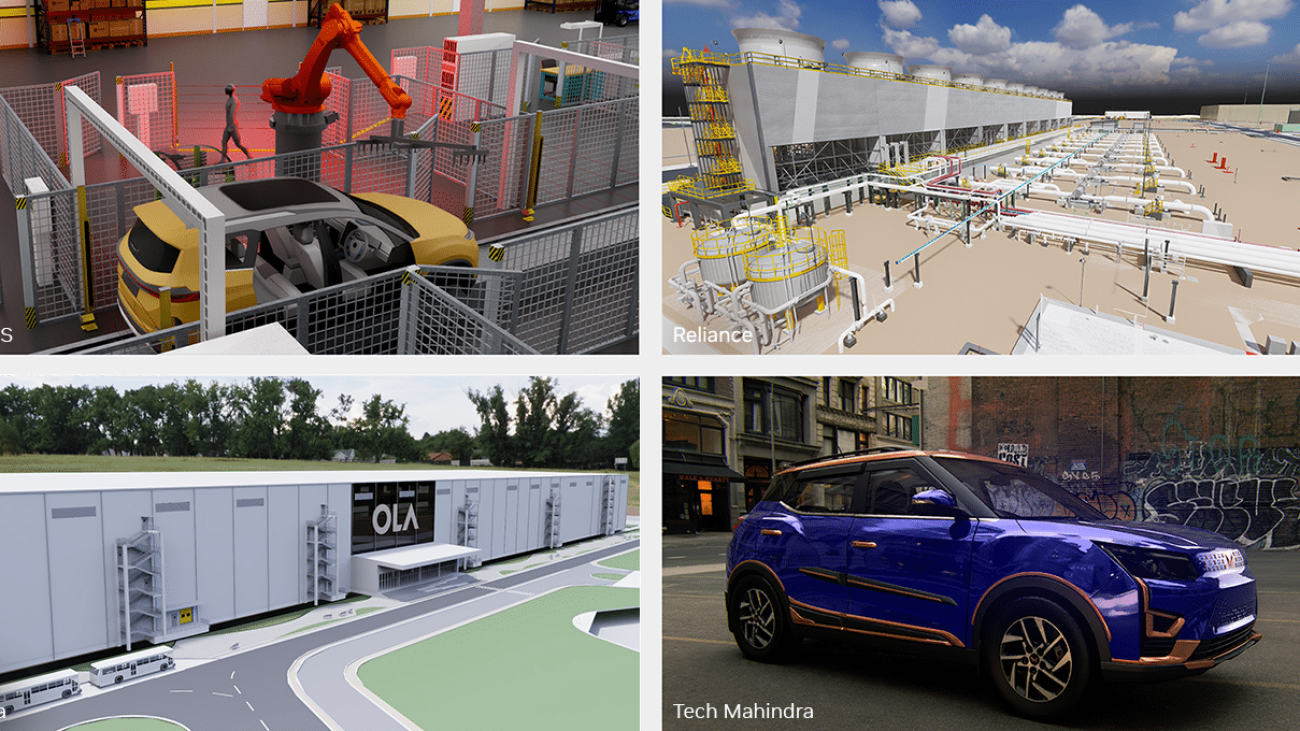
Manufacturers and service providers in India are adopting NVIDIA Omniverse to tap into simulation, digital twins and generative AI to accelerate their factory planning and drive automation for more efficient operations.
India’s exports have surged in recent years as the nation positions itself to be the next global industrial manufacturing powerhouse. Automotive, industrial machinery, electronics, textiles, chemicals and pharmaceuticals are among the sectors expected to help drive India’s exports to $1 trillion by 2028, according to Bain & Company.
As India’s manufacturing industry continues to soar, manufacturers are embracing AI for digitization of processes and robotics to scale their operations and meet growing global demands.
This wave of manufacturing automation, harnessing Omniverse to build virtual warehouses and production facilities to enable the next era of industrial and physical AI, was on full display this week at the NVIDIA AI Summit India, taking place in Mumbai through Oct. 25, from major industrial names like Ola Electric, Reliance Industries, Tech Mahindra, and TCS.
Ola Accelerates Electric Scooter Production With Omniverse
Ola Electric, the largest electric scooter maker in India, announced it has developed the Ola Digital Twin platform on NVIDIA Omniverse. The company said that the ODT platform has helped it achieve 20% faster time to market from design to commissioning for its manufacturing operations
Built on NVIDIA Isaac Sim, the Ola Digital Twin platform taps into core Omniverse technologies like OpenUSD for data interoperability, RTX for physically-based rendering, and generative AI for accelerated world building to generate synthetic data or training autonomous mobile robots and robotic arms.
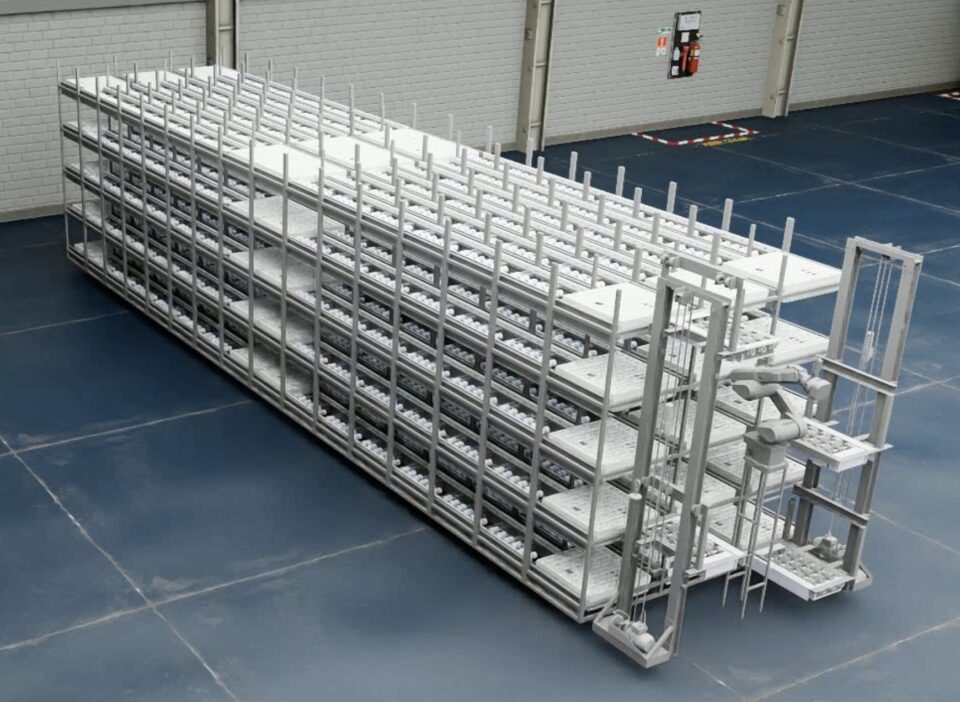

Ola is using the digital twin platform to plan and build its next-generation Future Factory — India’s largest integrated and automated electric two-wheeler manufacturing plant — in only eight months. The platform helped provide insights for factory and construction planning, as well as for quality inspection systems, manufacturing processes and safety training. The company is also using the digital twin to compare real and simulated environments, assisting with predictive maintenance.
Reliance Industries Adopts Omniverse for Solar Panel Factory Planning
Reliance Industries, a leading industrial conglomerate in India with businesses in energy, petrochemicals, natural gas, retail, entertainment, telecommunications, mass media and textiles, is embracing Omniverse for planning its new solar panel factory in Jamnagar, India.
Supporting the company’s goal of reaching net-zero carbon status by 2035, the 5,000-acre integrated photovoltaic manufacturing plant is meant to be India’s largest solar gigafactory.
Reliance is using Omniverse to develop applications for managing 3D data, virtual collaboration, simulation and optimized operations, as well as data integration for planning, design, automation, operation, sustainability and training of their workforce for soon to be commissioned Giga factories in Jamnagar, India.
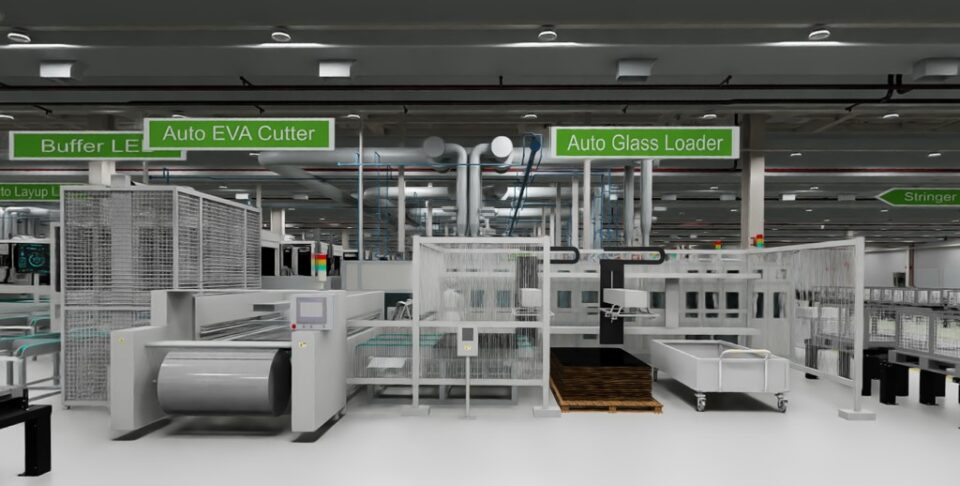

The company is also using Omniverse to develop OpenUSD-based, SimReady virtual factory assets, including the factory building, manufacturing equipment, robots, kinematics, and material and product models, and it’s running simulations for logistics and human workers.
Leading System Integrators Help India Manufacturers Embrace Industrial AI
System integrators play a crucial role in helping India’s largest manufacturers use NVIDIA technology to build the country’s next generation of manufacturing plants.
Consulting leaders such as Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) and Tech Mahindra are developing industrial AI applications and services on Omniverse to help manufacturers develop digital twins for accelerated factory planning, optimized processes, robotics training and large-scale automation.
TCS announced it’s working on a suite of digital twin solutions built on NVIDIA Omniverse that enable manufacturers to design, simulate, operate and optimize their products and production facilities across multiple sectors.
Use cases cover nearly every aspect of heavy manufacturing — from building virtual factories for real-time factory planning and monitoring, to creating digital twins of aircraft components for immersive training and predictive maintenance.
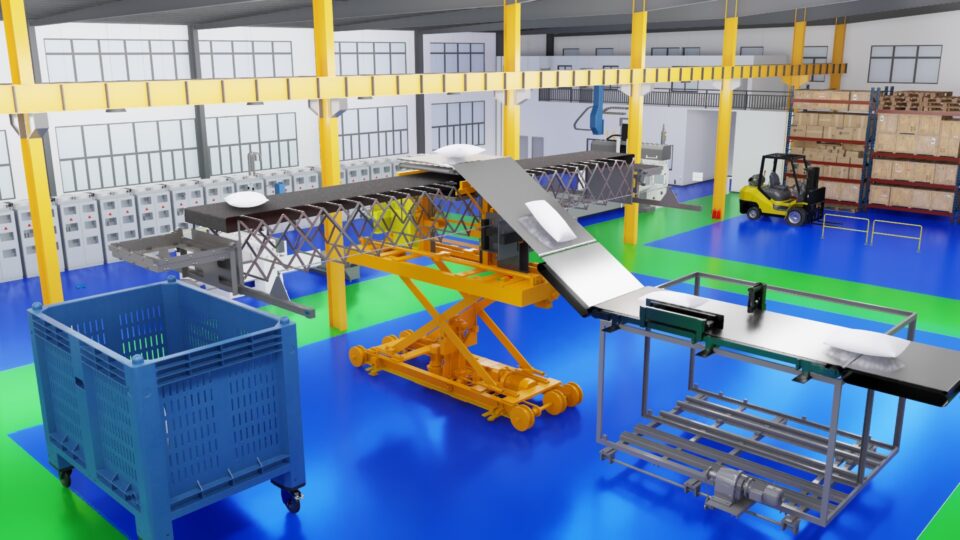

TCS also uses Omniverse to simulate autonomous vehicles, enabling automotive companies to simulate and validate complex driving scenarios without the need for physical testing. Meanwhile, its smart farming digital twin integrates real-world physics to simulate farming scenarios that help improve equipment performance.
In addition, TCS launched its TCS Manufacturing AI for Industrials, a generative AI solution built on the NVIDIA AI Enterprise platform, which includes NVIDIA NeMo for building and managing the AI application lifecycle, to turn general-purpose large language models (LLMs) into manufacturing expert AI agents capable of providing real-time, industry-specific insights across clients’ various production facilities. These agentic AIs can be connected to virtual factories, developed on Omniverse, to augment facility planning, design, and operations.
Tech Mahindra, a global leader in technology consulting, announced it is establishing a center of excellence enabled by NVIDIA AI Enterprise and Omniverse. It is targeted at helping drive advances in sovereign LLM frameworks, agentic AI and physical AI.

Tech Mahindra’s Center for Excellence uses NVIDIA Omniverse to develop connected industrial AI digital twins and physical AI applications for clients across sectors, including manufacturing, automotive, telecommunications, healthcare, banking, financial services and insurance.
Other leading system integrators such as Wipro and Infosys are also building solutions using the NVIDIA AI stack and expanding into physical AI with Omniverse.