The air is crisp, the pumpkins are waiting to be carved, and GFN Thursday is ready to deliver some gaming thrills.
GeForce NOW is unleashing a monster mash of gaming goodness this October with 22 titles joining the cloud, with five available for members to stream this week. From pulse-pounding action to immersive role-playing games, members’ cloud gaming cauldrons are about to bubble over with excitement. Plus, a new account portal update lets members take a look at their playtime details and history on GeForce NOW.
October Treats in Store
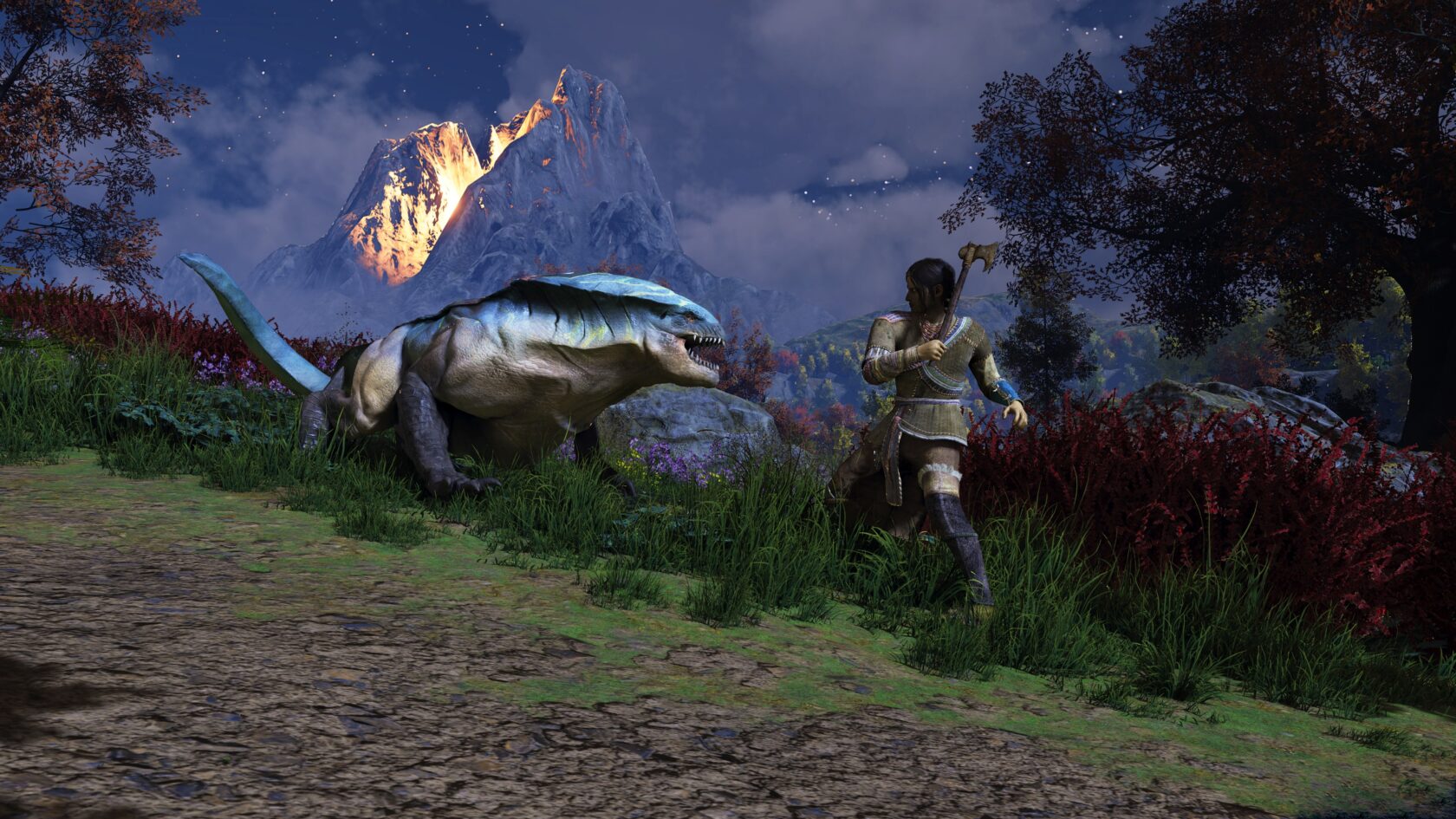
GeForce NOW is offering plenty of treats for members this month, starting with the launch of THRONE AND LIBERTY this week.

THRONE AND LIBERTY is a free-to-play massively multiplayer online role-playing game that takes place in the vast open world of Solisium. Scale expansive mountain ranges for new vantage points, scan open skies, traverse sprawling plains and explore a land full of depth and opportunity.
Adapt to survive and thrive through strategic decisions in player vs. player or player vs. environment combat modes while navigating evolving battlefields impacted by weather, time of day and other players. There’s no single path to victory to defeat Kazar and claim the throne while keeping rival guilds at bay.
Look for the following games available to stream in the cloud this week:
- THRONE AND LIBERTY (New release on Steam, Oct. 1)
- Sifu (Available on PC Game Pass, Oct. 2)
- Bear and Breakfast (Free on Epic Games Store, Oct. 3)
- Monster Jam Showdown (Steam)
- TerraTech Worlds (Steam)
Here’s what members can expect for the rest of October:
- Europa (New release on Steam, Oct. 11)
- Neva (New release on Steam, Oct. 15)
- MechWarrior 5: Clans (New release on Steam and Xbox, Oct. 16)
- A Quiet Place: The Road Ahead (New release on Steam, Oct. 17)
- Worshippers of Cthulhu (New release on Steam, Oct. 21)
- No More Room in Hell 2 (New release on Steam, Oct. 22)
- Romancing SaGa 2: Revenge of the Seven (New release on Steam, Oct. 24)
- Call of Duty: Black Ops 6 (New release on Steam and Battle.net, Oct. 25)
- Life Is Strange: Double Exposure (New release on Steam and Xbox, available in the Microsoft store, Oct. 29)
- Artisan TD (Steam)
- ASKA (Steam)
- DUCKSIDE (Steam)
- Dwarven Realms (Steam)
- Selaco (Steam)
- Spirit City: Lofi Sessions (Steam)
- Starcom: Unknown Space (Steam)
- Star Trek Timelines (Steam)
Surprises in September
In addition to the 18 games announced last month, 12 more joined the GeForce NOW library:
- Warhammer 40,000: Space Marine 2 (New release on Steam, Sept. 9)
- Dead Rising Deluxe Remaster (New release on Steam, Sept. 18)
- Witchfire (New release on Steam, Sept. 23)
- Monopoly (New release on Ubisoft Connect, Sept. 26)
- Dawn of Defiance (Steam)
- Flintlock: The Siege of Dawn (Xbox, available on PC Game Pass)
- Fort Solis (Epic Games Store)
- King Arthur: Legion IX (Steam)
- The Legend of Heroes: Trails Through Daybreak (Steam)
- Squirrel With a Gun (Steam)
- Tyranny – Gold Edition (Xbox, available on Microsoft Store)
- XIII (Xbox, available on Microsoft Store)
Blacksmith Simulator didn’t make it in September as the game’s launch was moved to next year.
What are you planning to play this weekend? Let us know on X or in the comments below.
What’s your favorite horror game?
—
NVIDIA GeForce NOW (@NVIDIAGFN) October 2, 2024




 Event Date: October 9, 2024
Event Date: October 9, 2024

 Pette will explain how NVIDIA’s accelerated computing platform enables advancements in sensor processing, autonomous systems, and digital twins. These AI applications offer wide-reaching benefits across industries.
Pette will explain how NVIDIA’s accelerated computing platform enables advancements in sensor processing, autonomous systems, and digital twins. These AI applications offer wide-reaching benefits across industries.