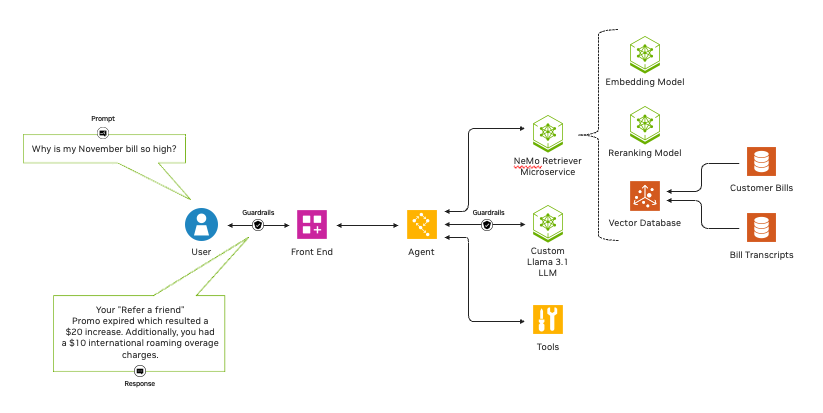
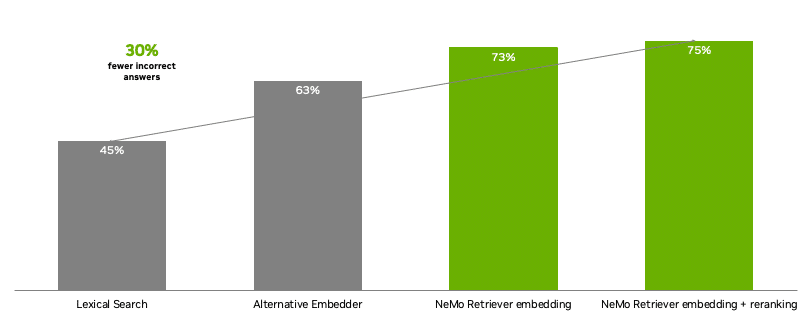
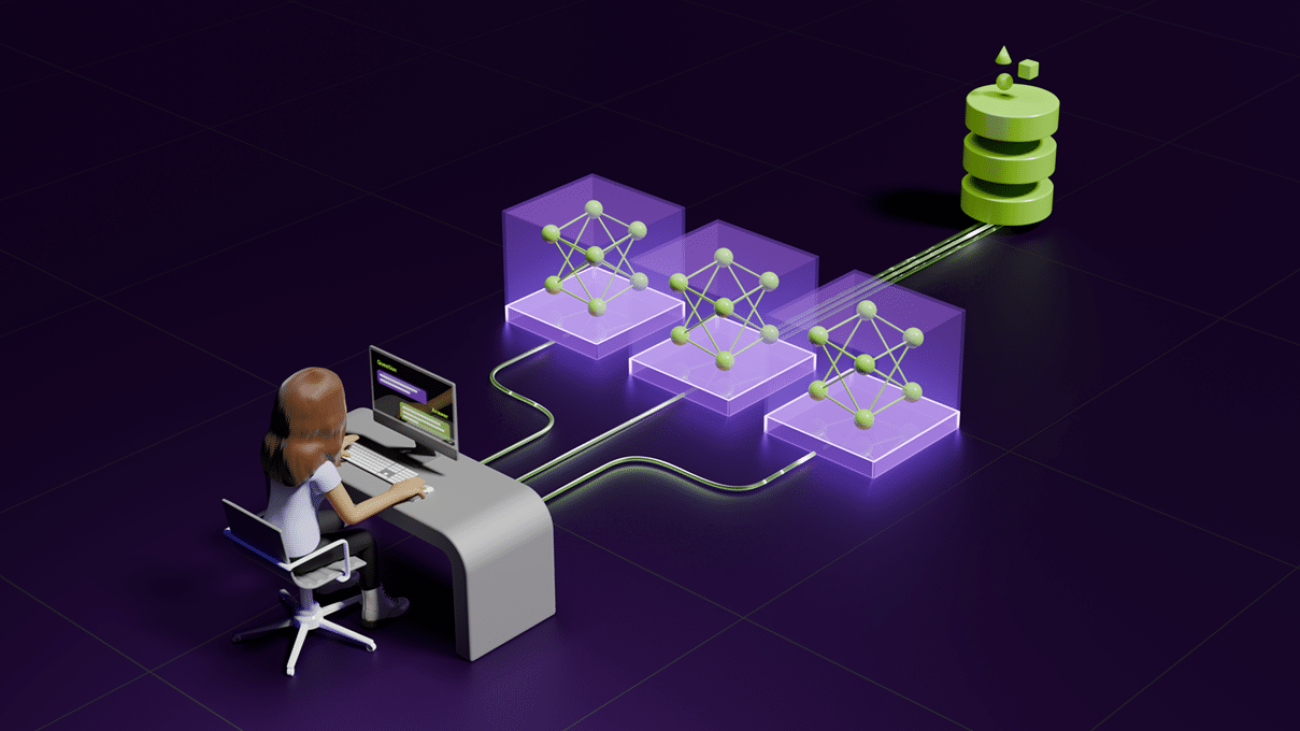
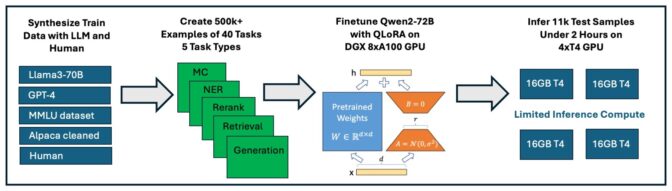
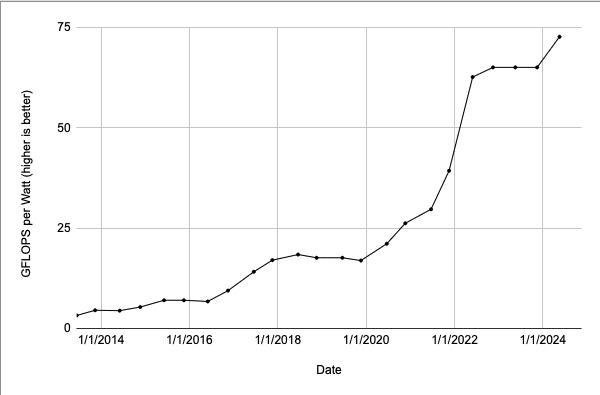
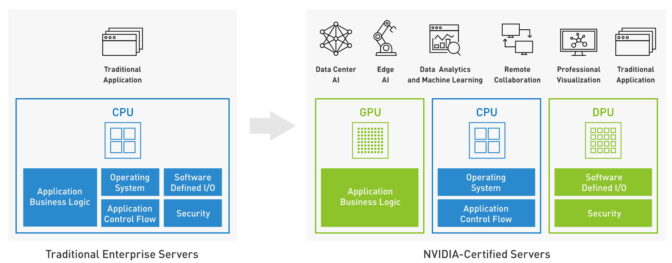
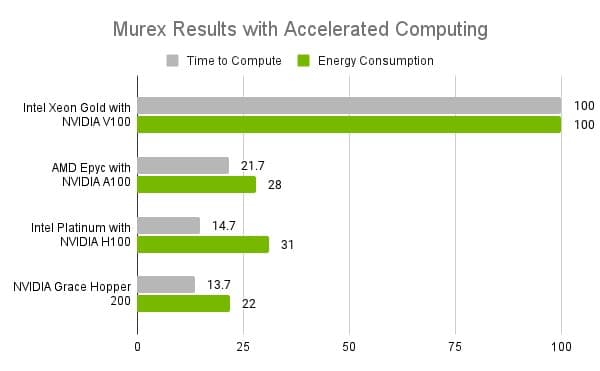
Generative AI is unlocking new ways for enterprises to engage customers through digital human avatars.
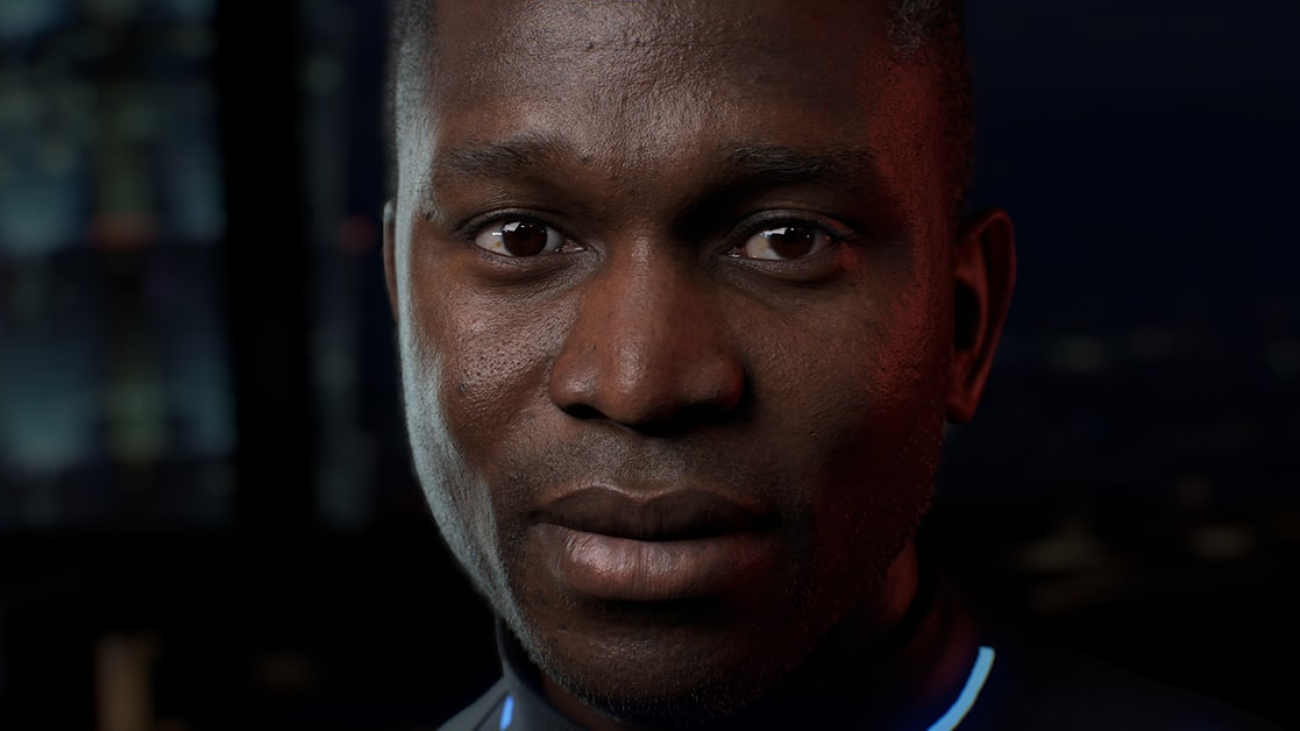
At SIGGRAPH, NVIDIA previewed “James,” an interactive digital human that can connect with people using emotions, humor and more. James is based on a customer-service workflow using NVIDIA ACE, a reference design for creating custom, hyperrealistic, interactive avatars. Users will soon be able to talk with James in real time at ai.nvidia.com.
NVIDIA also showcased at the computer graphics conference the latest advancements to the NVIDIA Maxine AI platform, including Maxine 3D and Audio2Face-2D for an immersive telepresence experience.
Developers can use Maxine and NVIDIA ACE digital human technologies to make customer interactions with digital interfaces more engaging and natural. ACE technologies enable digital human development with AI models for speech and translation, vision, intelligence, lifelike animation and behavior, and realistic appearance.
Companies across industries are using Maxine and ACE to deliver immersive virtual customer experiences.
Meet James, a Digital Brand Ambassador
Built on top of NVIDIA NIM microservices, James is a virtual assistant that can provide contextually accurate responses.
Using retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), James can accurately tell users about the latest NVIDIA technologies. ACE allows developers to use their own data to create domain-specific avatars that can communicate relevant information to customers.
James is powered by the latest NVIDIA RTX rendering technologies for advanced, lifelike animations. His natural-sounding voice is powered by ElevenLabs. NVIDIA ACE lets developers customize animation, voice and language when building avatars tailored for different use cases.
NVIDIA Maxine Enhances Digital Humans in Telepresence
Maxine, a platform for deploying cutting-edge AI features that enhance the audio and video quality of digital humans, enables the use of real-time, photorealistic 2D and 3D avatars with video-conferencing devices.
Maxine 3D converts 2D video portrait inputs into 3D avatars, allowing the integration of highly realistic digital humans in video conferencing and other two-way communication applications. The technology will soon be available in early access.
Audio2Face-2D, currently in early access, animates static portraits based on audio input, creating dynamic, speaking digital humans from a single image. Try the technology at ai.nvidia.com.
Companies Embracing Digital Human Applications
HTC, Looking Glass, Reply and UneeQ are among the latest companies using NVIDIA ACE and Maxine across a broad range of use cases, including customer service agents, and telepresence experiences in entertainment, retail and hospitality.
At SIGGRAPH, digital human technology developer UneeQ is showcasing two new demos.
The first spotlights cloud-rendered digital humans powered by NVIDIA GPUs with local, in-browser computer vision for enhanced scalability and privacy, and animated using the Audio2Face-3D NVIDIA NIM microservice. UneeQ’s Synapse technology processes anonymized user data and feeds it to a large language model (LLM) for more accurate, responsive interactions.
The second demo runs on a single NVIDIA RTX GPU-powered laptop, featuring an advanced digital human powered by Gemma 7B LLM, RAG and the NVIDIA Audio2Face-3D NIM microservice.
Both demos showcase UneeQ’s NVIDIA-powered efforts to develop digital humans that can react to users’ facial expressions and actions, pushing the boundaries of realism in virtual customer service experiences.
HTC Viverse has integrated the Audio2Face-3D NVIDIA NIM microservice into its VIVERSE AI agent for dynamic facial animation and lip sync, allowing for more natural and immersive user interactions.
Hologram technology company Looking Glass’ Magic Mirror demo at SIGGRAPH uses a simple camera setup and Maxine’s advanced 3D AI capabilities to generate a real-time holographic feed of users’ faces on its newly launched, group-viewable Looking Glass 16-inch and 32-inch Spatial Displays.
Reply is unveiling an enhanced version of Futura, its cutting-edge digital human developed for Costa Crociere’s Costa Smeralda cruise ship. Powered by Audio2Face-3D NVIDIA NIM and Riva ASR NIM microservices, Futura’s speech-synthesis capabilities tap advanced technologies including GPT-4o, LlamaIndex for RAG and Microsoft Azure text-to-speech services.
Futura also incorporates Reply’s proprietary affective computing technology, alongside Hume AI and MorphCast, for comprehensive emotion recognition. Built using Unreal Engine 5.4.3 and MetaHuman Creator with NVIDIA ACE-powered facial animation, Futura supports six languages. The intelligent assistant can help plan personalized port visits, suggest tailored itineraries and facilitate tour bookings.
In addition, Futura refines recommendations based on guest feedback and uses a specially created knowledge base to provide informative city presentations, enhancing tourist itineraries. Futura aims to enhance customer service and offer immersive interactions in real-world scenarios, leading to streamlined operations and driving business growth.
Learn more about NVIDIA ACE and NVIDIA Maxine.
Discover how accelerated computing and generative AI are transforming industries and creating new opportunities for innovation by watching NVIDIA founder and CEO Jensen Huang’s fireside chats at SIGGRAPH.
See notice regarding software product information.











 ʏᴏᴜʀ ᴄʟᴏᴜᴅ ɢᴀᴍɪɴɢ ꜱᴋɪʟʟ ɪɴᴄʀᴇᴀꜱᴇᴅ
ʏᴏᴜʀ ᴄʟᴏᴜᴅ ɢᴀᴍɪɴɢ ꜱᴋɪʟʟ ɪɴᴄʀᴇᴀꜱᴇᴅ NVIDIA GeForce NOW (@NVIDIAGFN)
NVIDIA GeForce NOW (@NVIDIAGFN)