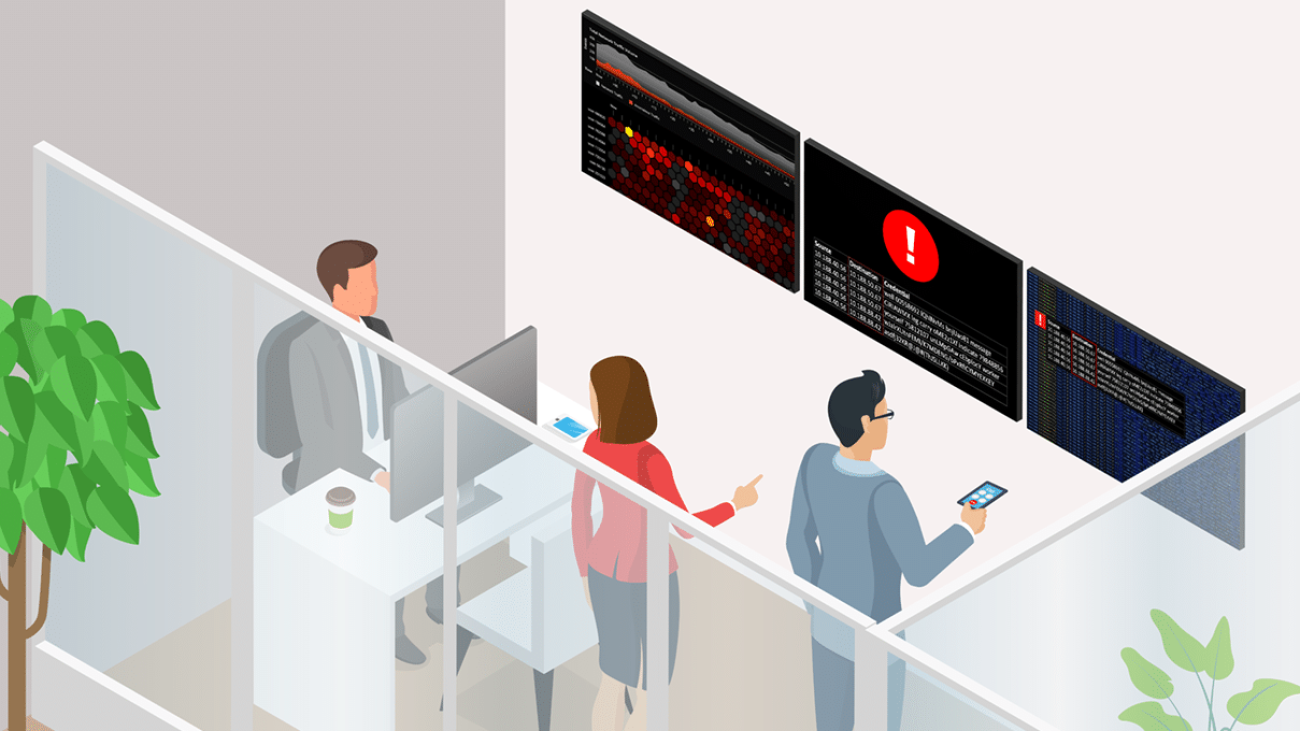
The world’s 5 billion internet users and nearly 54 billion devices generate 3.4 petabytes of data per second, according to IDC. As digitalization accelerates, enterprise IT teams are under greater pressure to identify and block incoming cyber threats to ensure business operations and services are not interrupted — and AI-based cybersecurity provides a reliable way to do so.
Few industries appear immune to cyber threats. This year alone, international hotel chains, financial institutions, Fortune 100 retailers, air traffic-control systems and the U.S. government have all reported threats and intrusions.
Whether from insider error, cybercriminals, hacktivists or other threats, risks in the cyber landscape can damage an enterprise’s reputation and bottom line. A breach can paralyze operations, jeopardize proprietary and customer data, result in regulatory fines and destroy customer trust.
Using AI and accelerated computing, businesses can reduce the time and operational expenses required to detect and block cyber threats while freeing up resources to focus on core business value operations and revenue-generating activities.
Here’s a look at how industries are applying AI techniques to safeguard data, enable faster threat detection and mitigate attacks to ensure the consistent delivery of service to customers and partners.
Public Sector: Protecting Physical Security, Energy Security and Citizen Services
AI-powered analytics and automation tools are helping government agencies provide citizens with instant access to information and services, make data-driven decisions, model climate change, manage natural disasters, and more. But public entities managing digital tools and infrastructure face a complex cyber risk environment that includes regulatory compliance requirements, public scrutiny, large interconnected networks and the need to protect sensitive data and high-value targets.
Adversary nation-states may initiate cyberattacks to disrupt networks, steal intellectual property or swipe classified government documents. Internal misuse of digital tools and infrastructure combined with sophisticated external espionage places public organizations at high risk of data breach. Espionage actors have also been known to recruit inside help, with 16% of public administration breaches showing evidence of collusion. To protect critical infrastructure, citizen data, public records and other sensitive information, federal organizations are turning to AI.
The U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Office of Cybersecurity, Energy Security and Emergency Response (CESER) is tasked with strengthening the resilience of the country’s energy sector by addressing emerging threats and improving energy infrastructure security. The DOE-CESER has invested more than $240 million in cybersecurity research, development and demonstration projects since 2010.
In one project, the department developed a tool that uses AI to automate and optimize security vulnerability and patch management in energy delivery systems. Another project for artificial diversity and defense security uses software-defined networks to enhance the situational awareness of energy delivery systems, helping ensure uninterrupted flows of energy.
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), which is charged with researching and investing in breakthrough technologies for national security, is using machine learning and AI in several areas. The DARPA CASTLE program trains AI to defend against advanced, persistent cyber threats. As part of the effort, researchers intend to accelerate cybersecurity assessments with approaches that are automated, repeatable and measurable. The DARPA GARD program builds platforms, libraries, datasets and training materials to help developers build AI models that are resistant to deception and adversarial attacks.
To keep up with an evolving threat landscape and ensure physical security, energy security and data security, public organizations must continue integrating AI to achieve a dynamic, proactive and far-reaching cyber defense posture.
Financial Services: Securing Digital Transactions, Payments and Portfolios
Banks, asset managers, insurers and other financial service organizations are using AI and machine learning to deliver superior performance in fraud detection, portfolio management, algorithmic trading and self-service banking.
With constant digital transactions, payments, loans and investment trades, financial service institutions manage some of the largest, most complex and most sensitive datasets of any industry. Behind only the healthcare industry, these organizations suffer the second highest cost of a data breach, at nearly $6 million per incident. This cost grows if regulators issue fines or if recovery includes legal fees and lawsuit settlements. Worse still, lost business may never be recovered if trust can’t be repaired.
Banks and financial institutions use AI to improve insider threat detection, detect phishing and ransomware, and keep sensitive information safe.
FinSec Innovation Lab, a joint venture by Mastercard and Enel X, is using AI to help its customers defend against ransomware. Prior to working with FinSec, one card-processing customer suffered a LockBit ransomware attack in which 200 company servers were infected in just 1.5 hours. The company was forced to shut down servers and suspend operations, resulting in an estimated $7 million in lost business.
FinSec replicated this attack in its lab but deployed the NVIDIA Morpheus cybersecurity framework, NVIDIA DOCA software framework for intrusion detection and NVIDIA BlueField DPU computing clusters. With this mix of AI and accelerated computing, FinSec was able to detect the ransomware attack in less than 12 seconds, quickly isolate virtual machines and recover 80% of the data on infected servers. This type of real-time response helps businesses avoid service downtime and lost business while maintaining customer trust.
With AI to help defend against cyberattacks, financial institutions can identify intrusions and anticipate future threats to keep financial records, accounts and transactions secure.
Retail: Keeping Sales Channels and Payment Credentials Safe
Retailers are using AI to power personalized product recommendations, dynamic pricing and customized marketing campaigns. Multichannel digital platforms have made in-store and online shopping more convenient: up to 48% of consumers save a card on file with a merchant, significantly boosting card-not-present transactions. While digitization has brought convenience, it has also made sensitive data more accessible to attackers.
Sitting on troves of digital payment credentials for millions of customers, retailers are a prime target for cybercriminals looking to take advantage of security gaps. According to a recent Data Breach Investigations Report from Verizon, 37% of confirmed data disclosures in the retail industry resulted in stolen payment card data.
Malware attacks, ransomware and distributed denial of service attacks are all on the rise, but phishing remains the favored vector for an initial attack. With a successful phishing intrusion, criminals can steal credentials, access systems and launch ransomware.
Best Buy manages a network of more than 1,000 stores across the U.S. and Canada. With multichannel digital sales across both countries, protecting consumer information and transactions is critical. To defend against phishing and other cyber threats, Best Buy began using customized machine learning and NVIDIA Morpheus to better secure their infrastructure and inform their security analysts.
After deploying this AI-based cyber defense, the retail giant improved the accuracy of phishing detection to 96% while reducing false-positive rates. With a proactive approach to cybersecurity, Best Buy is protecting its reputation as a tech expert focused on customer needs.
From complex supply chains to third-party vendors and multichannel point-of-sale networks, expect retailers to continue integrating AI to protect operations as well as critical proprietary and customer data.
Smart Cities and Spaces: Protecting Critical Infrastructure and Transit Networks
IoT devices and AI that analyze movement patterns, traffic and hazardous situations have great potential to improve the safety and efficiency of spaces and infrastructure. But as airports, shipping ports, transit networks and other smart spaces integrate IoT and use data, they also become more vulnerable to attack.
In the last couple of years, there have been distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks on airports and air traffic control centers and ransomware attacks on seaports, city municipalities, police departments and more. Attacks can paralyze information systems, ground flights, disrupt the flow of cargo and traffic, and delay the delivery of goods to markets. Hostile attacks could have far more serious consequences, including physical harm or loss of life.
In connected spaces, AI-driven security can analyze vast amounts of data to predict threats, isolate attacks and provide rapid self-healing after an intrusion. AI algorithms trained on emails can halt threats in the inbox and block phishing attempts like those that delivered ransomware to seaports earlier this year. Machine learning can be trained to recognize DDoS attack patterns to prevent the type of incoming malicious traffic that brought down U.S. airport websites last year.
Organizations adopting smart space technology, such as the Port of Los Angeles, are making efforts to get ahead of the threat landscape. In 2014, the Port of LA established a cybersecurity operations center and hired a dedicated cybersecurity team. In 2021, the port followed up with a cyber resilience center to enhance early-warning detection for cyberattacks that have the potential to impact the flow of cargo.
The U.S. Federal Aviation Administration has developed an AI certification framework that assesses the trustworthiness of AI and ML applications. The FAA also implements a zero-trust cyber approach, enforces strict access control and runs continuous verification across its digital environment.
By bolstering cybersecurity and integrating AI, smart space and transport infrastructure administrators can offer secure access to physical spaces and digital networks to protect the uninterrupted movement of people and goods.
Telecommunications: Ensure Network Resilience and Block Incoming Threats
Telecommunications companies are leaning into AI to power predictive maintenance and maximum network uptime, network optimization, equipment troubleshooting, call-routing and self-service systems.
The industry is responsible for critical national infrastructure in every country, supports over 5 billion customer endpoints and is expected to constantly deliver above 99% reliability. As reliance on cloud, IoT and edge computing expands and 5G becomes the norm, immense digital surface areas must be protected from misuse and malicious attack.
Telcos can deploy AI to ensure the security and resilience of networks. AI can monitor IoT devices and edge networks to detect anomalies and intrusions, identify fake users, mitigate attacks and quarantine infected devices. AI can continuously assess the trustworthiness of devices, users and applications, thereby shortening the time needed to identify fraudsters.
Pretrained AI models can be deployed to protect 5G networks from threats such as malware, data exfiltration and DOS attacks.
Using deep learning and NVIDIA BlueField DPUs, Palo Alto Networks has built a next-generation firewall addressing 5G needs, maximizing cybersecurity performance while maintaining a small infrastructure footprint. The DPU powers accelerated intelligent network filtering to parse, classify and steer traffic to improve performance and isolate threats. With more efficient computing that deploys fewer servers, telcos can maximize return on investment for compute investments and minimize digital attack surface areas.
By putting AI to work, telcos can build secure, encrypted networks to ensure network availability and data security for both individual and enterprise customers.
Automotive: Insulate Vehicle Software From Outside Influence and Attack
Modern cars rely on complex AI and ML software stacks running on in-vehicle computers to process data from cameras and other sensors. These vehicles are essentially giant, moving IoT devices — they perceive the environment, make decisions, advise drivers and even control the vehicle with autonomous driving features.
Like other connected devices, autonomous vehicles are susceptible to various types of cyberattacks. Bad actors can infiltrate and compromise AV software both on board and from third-party providers. Denial of service attacks can disrupt over-the-air software updates that vehicles rely on to operate safely. Unauthorized access to communications systems like onboard WiFi, Bluetooth or RFID can expose vehicle systems to the risk of remote manipulation and data theft. This can jeopardize geolocation and sensor data, operational data, driver and passenger data, all of which are crucial to functional safety and the driving experience.
AI-based cybersecurity can help monitor in-car and network activities in real time, allowing for rapid response to threats. AI can be deployed to secure and authenticate over-the-air updates to prevent tampering and ensure the authenticity of software updates. AI-driven encryption can protect data transmitted over WiFi, Bluetooth and RFID connections. AI can also probe vehicle systems for vulnerabilities and take remedial steps.
Ranging from AI-powered access control to unlock and start vehicles to detecting deviations in sensor performance and patching security vulnerabilities, AI will play a crucial role in the safe development and deployment of autonomous vehicles on our roads.
Keeping Operations Secure and Customers Happy With AI Cybersecurity
By deploying AI to protect valuable data and digital operations, industries can focus their resources on innovating better products, improving customer experiences and creating new business value.
NVIDIA offers a number of tools and frameworks to help enterprises swiftly adjust to the evolving cyber risk environment. The NVIDIA Morpheus cybersecurity framework provides developers and software vendors with optimized, easy-to-use tools to build solutions that can proactively detect and mitigate threats while drastically reducing the cost of cyber defense operations. To help defend against phishing attempts, the NVIDIA spear phishing detection AI workflow uses NVIDIA Morpheus and synthetic training data created with the NVIDIA NeMo generative AI framework to flag and halt inbox threats.
The Morpheus SDK also enables digital fingerprinting to collect and analyze behavior characteristics for every user, service, account and machine across a network to identify atypical behavior and alert network operators. With the NVIDIA DOCA software framework, developers can create software-defined, DPU-accelerated services, while leveraging zero trust to build more secure applications.
AI-based cybersecurity empowers developers across industries to build solutions that can identify, capture and act on threats and anomalies to ensure business continuity and uninterrupted service, keeping operations safe and customers happy.
Learn how AI can help your organization achieve a proactive cybersecurity posture to protect customer and proprietary data to the highest standards.









 NVIDIA GeForce NOW (@NVIDIAGFN)
NVIDIA GeForce NOW (@NVIDIAGFN)