MLPerf remains the definitive measurement for AI performance as an independent, third-party benchmark. NVIDIA’s AI platform has consistently shown leadership across both training and inference since the inception of MLPerf, including the MLPerf Inference 3.0 benchmarks released today.
“Three years ago when we introduced A100, the AI world was dominated by computer vision. Generative AI has arrived,” said NVIDIA founder and CEO Jensen Huang.
“This is exactly why we built Hopper, specifically optimized for GPT with the Transformer Engine. Today’s MLPerf 3.0 highlights Hopper delivering 4x more performance than A100.
“The next level of Generative AI requires new AI infrastructure to train large language models with great energy efficiency. Customers are ramping Hopper at scale, building AI infrastructure with tens of thousands of Hopper GPUs connected by NVIDIA NVLink and InfiniBand.
“The industry is working hard on new advances in safe and trustworthy Generative AI. Hopper is enabling this essential work,” he said.
The latest MLPerf results show NVIDIA taking AI inference to new levels of performance and efficiency from the cloud to the edge.
Specifically, NVIDIA H100 Tensor Core GPUs running in DGX H100 systems delivered the highest performance in every test of AI inference, the job of running neural networks in production. Thanks to software optimizations, the GPUs delivered up to 54% performance gains from their debut in September.
In healthcare, H100 GPUs delivered a 31% performance increase since September on 3D-UNet, the MLPerf benchmark for medical imaging.
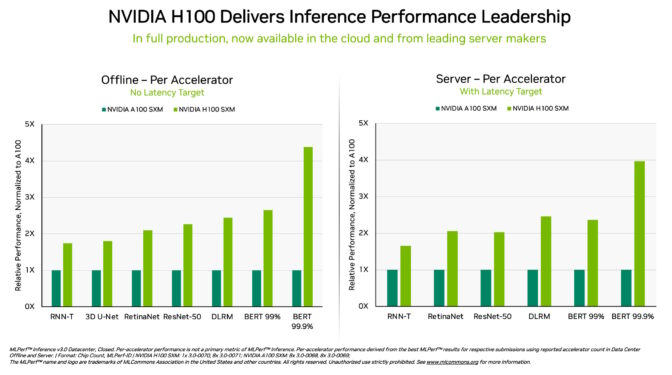
Powered by its Transformer Engine, the H100 GPU, based on the Hopper architecture, excelled on BERT, a transformer-based large language model that paved the way for today’s broad use of generative AI.
Generative AI lets users quickly create text, images, 3D models and more. It’s a capability companies from startups to cloud service providers are rapidly adopting to enable new business models and accelerate existing ones.
Hundreds of millions of people are now using generative AI tools like ChatGPT — also a transformer model — expecting instant responses.
At this iPhone moment of AI, performance on inference is vital. Deep learning is now being deployed nearly everywhere, driving an insatiable need for inference performance from factory floors to online recommendation systems.
L4 GPUs Speed Out of the Gate
NVIDIA L4 Tensor Core GPUs made their debut in the MLPerf tests at over 3x the speed of prior-generation T4 GPUs. Packaged in a low-profile form factor, these accelerators are designed to deliver high throughput and low latency in almost any server.
L4 GPUs ran all MLPerf workloads. Thanks to their support for the key FP8 format, their results were particularly stunning on the performance-hungry BERT model.
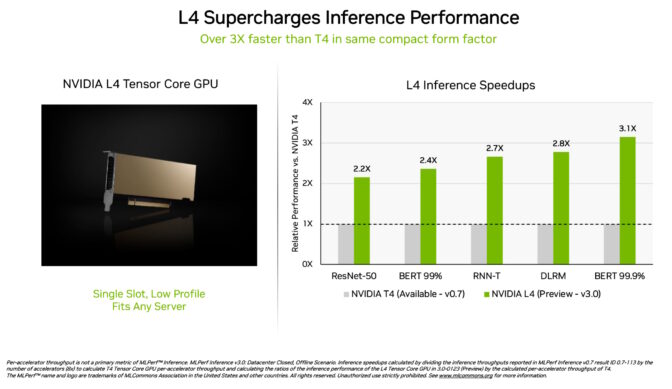
In addition to stellar AI performance, L4 GPUs deliver up to 10x faster image decode, up to 3.2x faster video processing and over 4x faster graphics and real-time rendering performance.
Announced two weeks ago at GTC, these accelerators are already available from major systems makers and cloud service providers. L4 GPUs are the latest addition to NVIDIA’s portfolio of AI inference platforms launched at GTC.
Software, Networks Shine in System Test
NVIDIA’s full-stack AI platform showed its leadership in a new MLPerf test.
The so-called network-division benchmark streams data to a remote inference server. It reflects the popular scenario of enterprise users running AI jobs in the cloud with data stored behind corporate firewalls.
On BERT, remote NVIDIA DGX A100 systems delivered up to 96% of their maximum local performance, slowed in part because they needed to wait for CPUs to complete some tasks. On the ResNet-50 test for computer vision, handled solely by GPUs, they hit the full 100%.
Both results are thanks, in large part, to NVIDIA Quantum Infiniband networking, NVIDIA ConnectX SmartNICs and software such as NVIDIA GPUDirect.
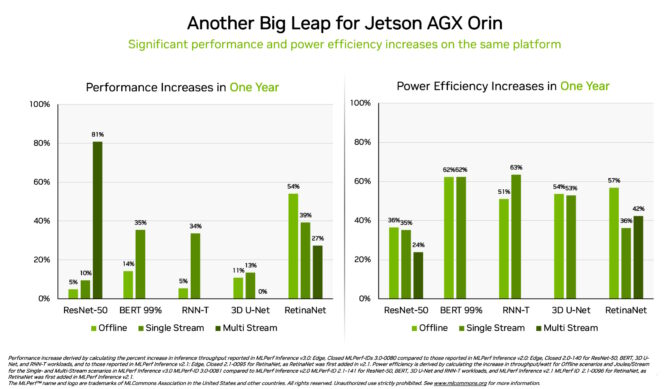
Orin Shows 3.2x Gains at the Edge
Separately, the NVIDIA Jetson AGX Orin system-on-module delivered gains of up to 63% in energy efficiency and 81% in performance compared with its results a year ago. Jetson AGX Orin supplies inference when AI is needed in confined spaces at low power levels, including on systems powered by batteries.
For applications needing even smaller modules drawing less power, the Jetson Orin NX 16G shined in its debut in the benchmarks. It delivered up to 3.2x the performance of the prior-generation Jetson Xavier NX processor.
A Broad NVIDIA AI Ecosystem
The MLPerf results show NVIDIA AI is backed by the industry’s broadest ecosystem in machine learning.
Ten companies submitted results on the NVIDIA platform in this round. They came from the Microsoft Azure cloud service and system makers including ASUS, Dell Technologies, GIGABYTE, H3C, Lenovo, Nettrix, Supermicro and xFusion.
Their work shows users can get great performance with NVIDIA AI both in the cloud and in servers running in their own data centers.
NVIDIA partners participate in MLPerf because they know it’s a valuable tool for customers evaluating AI platforms and vendors. Results in the latest round demonstrate that the performance they deliver today will grow with the NVIDIA platform.
Users Need Versatile Performance
NVIDIA AI is the only platform to run all MLPerf inference workloads and scenarios in data center and edge computing. Its versatile performance and efficiency make users the real winners.
Real-world applications typically employ many neural networks of different kinds that often need to deliver answers in real time.
For example, an AI application may need to understand a user’s spoken request, classify an image, make a recommendation and then deliver a response as a spoken message in a human-sounding voice. Each step requires a different type of AI model.
The MLPerf benchmarks cover these and other popular AI workloads. That’s why the tests ensure IT decision makers will get performance that’s dependable and flexible to deploy.
Users can rely on MLPerf results to make informed buying decisions, because the tests are transparent and objective. The benchmarks enjoy backing from a broad group that includes Arm, Baidu, Facebook AI, Google, Harvard, Intel, Microsoft, Stanford and the University of Toronto.
Software You Can Use
The software layer of the NVIDIA AI platform, NVIDIA AI Enterprise, ensures users get optimized performance from their infrastructure investments as well as the enterprise-grade support, security and reliability required to run AI in the corporate data center.
All the software used for these tests is available from the MLPerf repository, so anyone can get these world-class results.
Optimizations are continuously folded into containers available on NGC, NVIDIA’s catalog for GPU-accelerated software. The catalog hosts NVIDIA TensorRT, used by every submission in this round to optimize AI inference.
Read this technical blog for a deeper dive into the optimizations fueling NVIDIA’s MLPerf performance and efficiency.






 NVIDIA GeForce NOW (@NVIDIAGFN)
NVIDIA GeForce NOW (@NVIDIAGFN)