No Thursday is complete without GFN Thursday, our weekly celebration of the news, updates and great games GeForce NOW members can play — all streaming from the cloud across nearly all of your devices.
This week’s exciting updates to the GeForce NOW app and experience Include updated features, faster session loading and a bunch of new games joining the GFN library.
… Better, Faster, Stronger
There’s a lot happening behind the scenes as our team continuously works to improve your cloud-gaming experience with each session.
Our cloud-gaming engineers work to further improve your streaming sessions, optimize games and develop new features. We also continually refine the user experience in the GeForce NOW app, which is now rolling out version 2.0.29 with several improvements.
Game in the Fast Lane
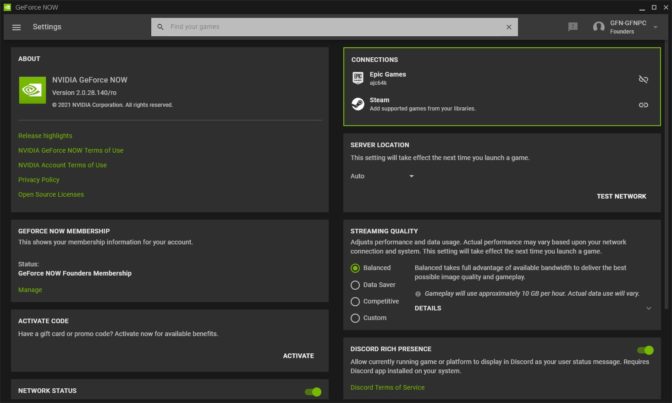
One feature we’re currently testing with our Founders and Priority members is preloading, which loads parts of your game before you arrive so your launch times will be faster. Members testing this feature should see sessions launch up to a minute faster from the moment they click play in the GeForce NOW app. Free members are not guaranteed preloaded sessions and may see slightly longer startup times.
To enable the benefits of preloading, we’re also testing a new account linking feature which lets you play games without having to login into your game store account. Both the preloading and account linking features are currently enabled for Fortnite’s PC build on GeForce NOW. We anticipate an expansion of these features to more GeForce NOW games in the future.
PC, macOS and Chromebook users can enable the new account linking features from a new tile on the My Library row in-app. This takes you to the Settings pane, where you can turn on account linking for Fortnite under Connections. Once complete, you won’t need to log in to your Epic Account to play Fortnite’s PC build on any other supported GeForce NOW platform, and you’ll be eligible for preloaded sessions.
Find What You’re Looking For
We’re also improving search results in the app to make managing libraries easier and get members in games faster. Searching for games to add to libraries will now return full page search results, providing easier access to the game’s details and a quicker way to add it to your library.
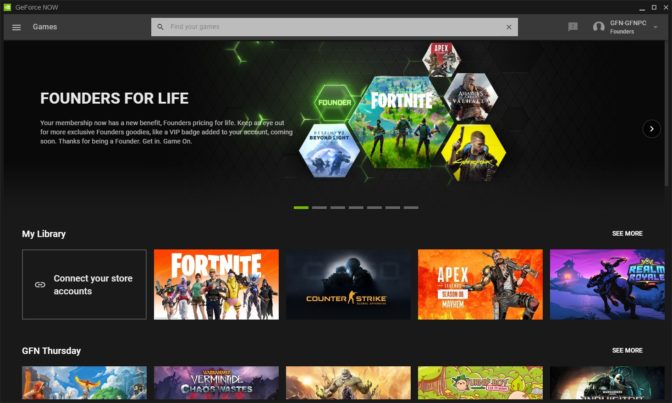
If you’re playing on GeForce NOW from a Chrome browser, we’ve recently added our in-game overlay. The overlay lets members configure many in-stream features, such as FreeStyle filters, network labels, microphone toggles and ending game sessions. To bring up the overlay, using Ctrl + G for PC and Chromebook, or CMD + G for macOS.
And no GeForce NOW app update would be complete without squashed bugs. To get the full lowdown, check out the version 2.0.29 Release Highlights from the Settings pane in the app.
These updates are just a few of the improvements we’re working on. We have a ton more in store, and every update is designed to make sure that when GFN members play their favorite PC games from our cloud servers, they’re getting the best possible experience.
Rolling in the Deep (Silver)
We recently spoke with our friends at Deep Silver about new updates coming for KING Art Games’ Iron Harvest and 4A Games’ Metro Exodus: Enhanced Edition, both of which will be supported on GeForce NOW. Catch up on all the details here.
Get Your Game On

Finally, below are the games joining the GeForce NOW library this week.
- R-Type Final 2 (day-and-date release on Steam)
- Chinese Parents (Steam)
- Darksiders II Deathinitive Edition (Epic Games Store)
- The Dungeon Of Naheulbeuk: The Amulet Of Chaos (Epic Games Store)
- GoNNER (Epic Games Store)
- SOMA (Epic Games Store)
- Yooka-Laylee and the Impossible Lair (Epic Games Store)
What do you think of the newest GeForce NOW updates? Let us know on Twitter or in the comments below.
The post Update Complete: GFN Thursday Brings New Features, Games and More appeared first on The Official NVIDIA Blog.