Looking directly at the sun isn’t recommended — unless you’re doing it with AI, which is what NASA is working on.
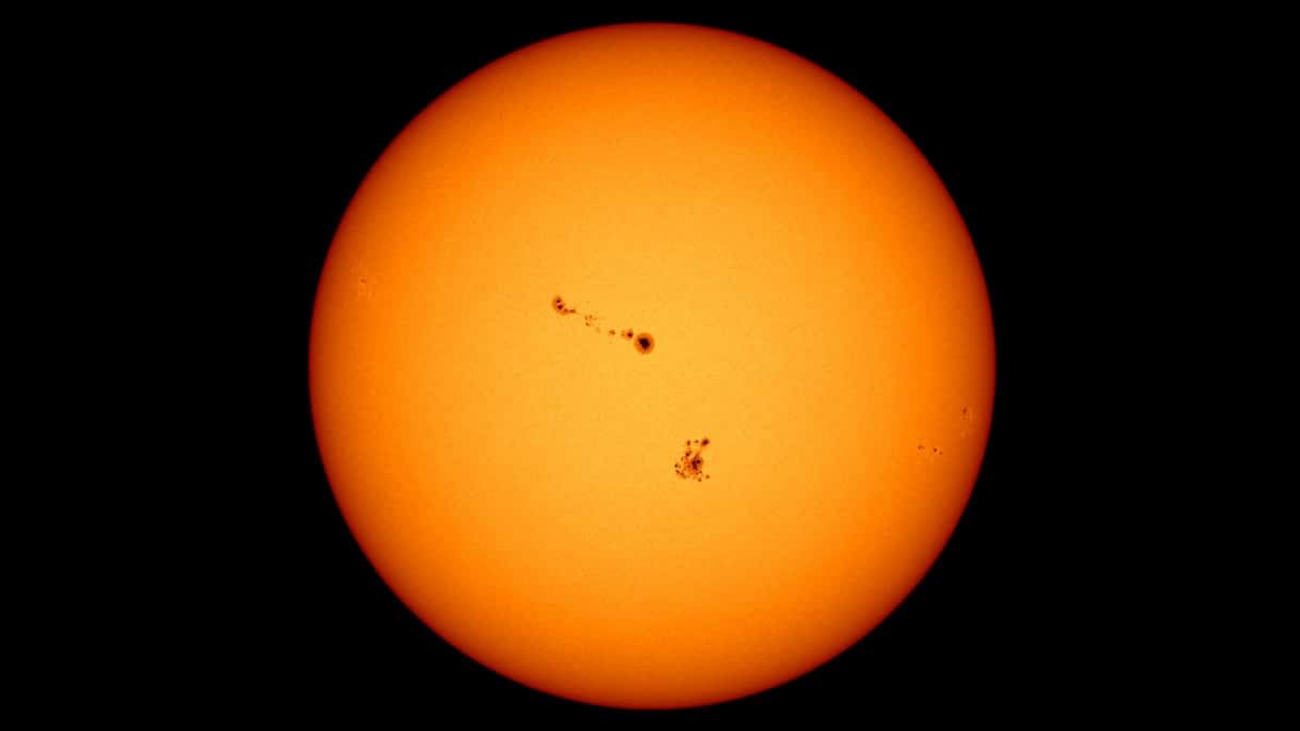
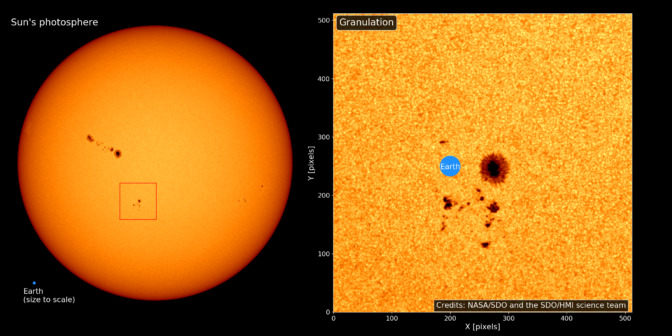
The surface of the sun, which is the layer you can see with the eye, is actually bubbly: intense heat creates a boiling reaction, similar to water at high temperature. So when NASA researchers magnify images of the sun with a telescope, they can see tiny blobs, called granules, moving on the surface.
Studying the movement and flows of the granules helps the researchers better understand what’s happening underneath that outer layer of the sun.
The computations for tracking the motion of granules requires advanced imaging techniques. Using data science and GPU computing with NVIDIA Quadro RTX-powered HP Z8 workstations, NASA researchers have developed deep learning techniques to more easily track the flows on the sun’s surface.
RTX Flares Up Deep Learning Performance
When studying how storms and hurricanes form, meteorologists analyze the flows of winds in Earth’s atmosphere. For this same reason, it’s important to measure the flows of plasma in the sun’s atmosphere to learn more about the short- and long-term evolution of our nearest star.
This helps NASA understand and anticipate events like solar flares, which can affect power grids, communication systems like GPS or radios, or even put space travel at risk because of the intense radiation and charged particles associated with space weather.
“It’s like predicting earthquakes,” said Michael Kirk, research astrophysicist at NASA. “Since we can’t see very well beneath the surface of the sun, we have to take measurements from the flows on the exterior to infer what is happening subsurface.”
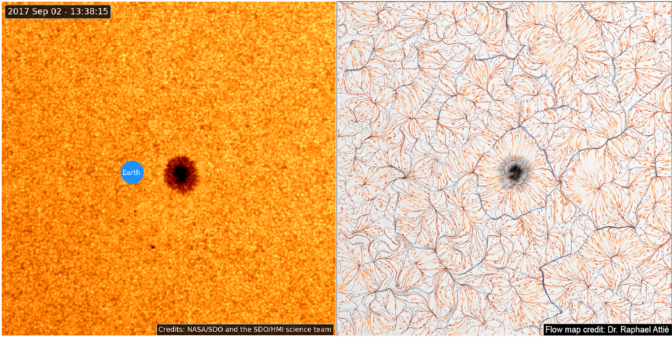
Granules are transported by plasma motions — hot ionized gas under the surface. To capture these motions, NASA developed customized algorithms best tailored to their solar observations, with a deep learning neural network that observes the granules using images from the Solar Dynamics Observatory, and then learns how to reconstruct their motions.
“Neural networks can generate estimates of plasma motions at resolutions beyond what traditional flow tracking methods can achieve,” said Benoit Tremblay from the National Solar Observatory. “Flow estimates are no longer limited to the surface — deep learning can look for a relationship between what we see on the surface and the plasma motions at different altitudes in the solar atmosphere.”
“We’re training neural networks using synthetic images of these granules to learn the flow fields, so it helps us understand precursor environments that surround the active magnetic regions that can become the source of solar flares,” said Raphael Attie, solar astronomer at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center.
NVIDIA GPUs were essential in training the neural networks because NASA needed to complete several training sessions with data preprocessed in multiple ways to develop robust deep learning models, and CPU power was not enough for these computations.
When using TensorFlow on a 72 CPU-core compute node, it took an hour to complete only one pass with the training data. Even in a CPU-based cloud environment, it would still take weeks to train all the models that the scientists needed for a single project.
With an NVIDIA Quadro RTX 8000 GPU, the researchers can complete one training in about three minutes — a 20x speedup. This allows them to start testing the trained models after a day instead of having to wait weeks.
“This incredible speedup enables us to try out different ways to train the models and make ‘stress tests,’ like preprocessing images at different resolutions or introducing synthetic errors to better emulate imperfections in the telescopes,” said Attie. “That kind of accelerated workflow completely changed the scope of what we can afford to explore, and it allows us to be much more daring and creative.”
With NVIDIA Quadro RTX GPUs, the NASA researchers can accelerate workflows for their solar physics projects, and they have more time to conduct thorough research with simulations to gain deeper understandings of the sun’s dynamics.
Learn more about NVIDIA and HP data science workstations, and listen to the AI Podcast with NASA.
The post Rise and Sunshine: NASA Uses Deep Learning to Map Flows on Sun’s Surface, Predict Solar Flares appeared first on The Official NVIDIA Blog.