Editor’s note: This post is part of the AI Decoded series, which demystifies AI by making the technology more accessible, and showcases new hardware, software, tools and accelerations for GeForce RTX PC and NVIDIA RTX workstation users.
Large language models (LLMs) are reshaping productivity. They’re capable of drafting documents, summarizing web pages and, having been trained on vast quantities of data, accurately answering questions about nearly any topic.
LLMs are at the core of many emerging use cases in generative AI, including digital assistants, conversational avatars and customer service agents.
Many of the latest LLMs can run locally on PCs or workstations. This is useful for a variety of reasons: users can keep conversations and content private on-device, use AI without the internet, or simply take advantage of the powerful NVIDIA GeForce RTX GPUs in their system. Other models, because of their size and complexity, do no’t fit into the local GPU’s video memory (VRAM) and require hardware in large data centers.
However, Iit i’s possible to accelerate part of a prompt on a data-center-class model locally on RTX-powered PCs using a technique called GPU offloading. This allows users to benefit from GPU acceleration without being as limited by GPU memory constraints.
Size and Quality vs. Performance
There’s a tradeoff between the model size and the quality of responses and the performance. In general, larger models deliver higher-quality responses, but run more slowly. With smaller models, performance goes up while quality goes down.
This tradeoff isn’t always straightforward. There are cases where performance might be more important than quality. Some users may prioritize accuracy for use cases like content generation, since it can run in the background. A conversational assistant, meanwhile, needs to be fast while also providing accurate responses.
The most accurate LLMs, designed to run in the data center, are tens of gigabytes in size, and may not fit in a GPU’s memory. This would traditionally prevent the application from taking advantage of GPU acceleration.
However, GPU offloading uses part of the LLM on the GPU and part on the CPU. This allows users to take maximum advantage of GPU acceleration regardless of model size.
Optimize AI Acceleration With GPU Offloading and LM Studio
LM Studio is an application that lets users download and host LLMs on their desktop or laptop computer, with an easy-to-use interface that allows for extensive customization in how those models operate. LM Studio is built on top of llama.cpp, so it’s fully optimized for use with GeForce RTX and NVIDIA RTX GPUs.
LM Studio and GPU offloading takes advantage of GPU acceleration to boost the performance of a locally hosted LLM, even if the model can’t be fully loaded into VRAM.
With GPU offloading, LM Studio divides the model into smaller chunks, or “subgraphs,” which represent layers of the model architecture. Subgraphs aren’t permanently fixed on the GPU, but loaded and unloaded as needed. With LM Studio’s GPU offloading slider, users can decide how many of these layers are processed by the GPU.
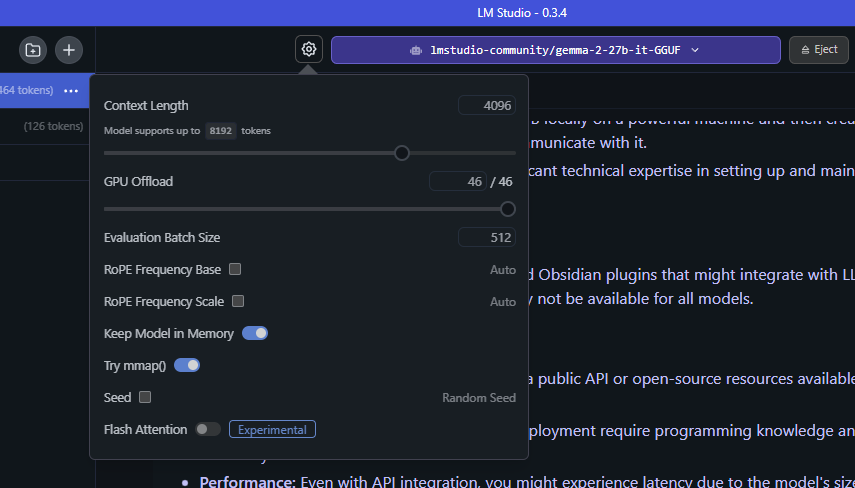
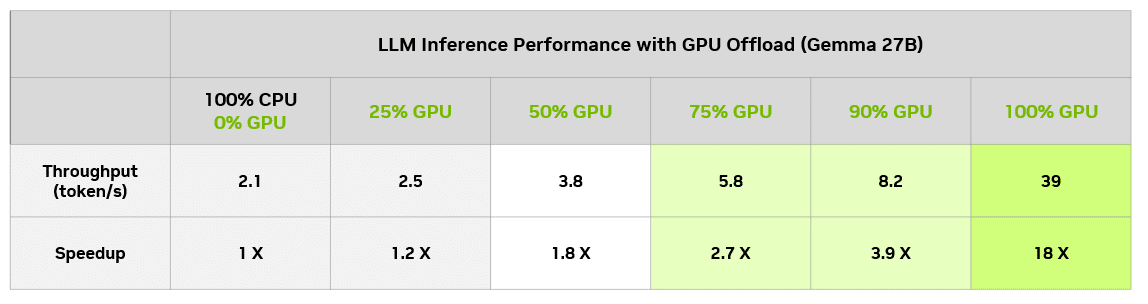
For example, imagine using this GPU offloading technique with a large model like Gemma 2 27B. “27B” refers to the number of parameters in the model, informing an estimate as to how much memory is required to run the model.
According to 4-bit quantization, a technique for reducing the size of an LLM without significantly reducing accuracy, each parameter takes up a half byte of memory. This means that the model should require about 13.5 billion bytes, or 13.5GB — plus some overhead, which generally ranges from 1-5GB.
Accelerating this model entirely on the GPU requires 19GB of VRAM, available on the GeForce RTX 4090 desktop GPU. With GPU offloading, the model can run on a system with a lower-end GPU and still benefit from acceleration.
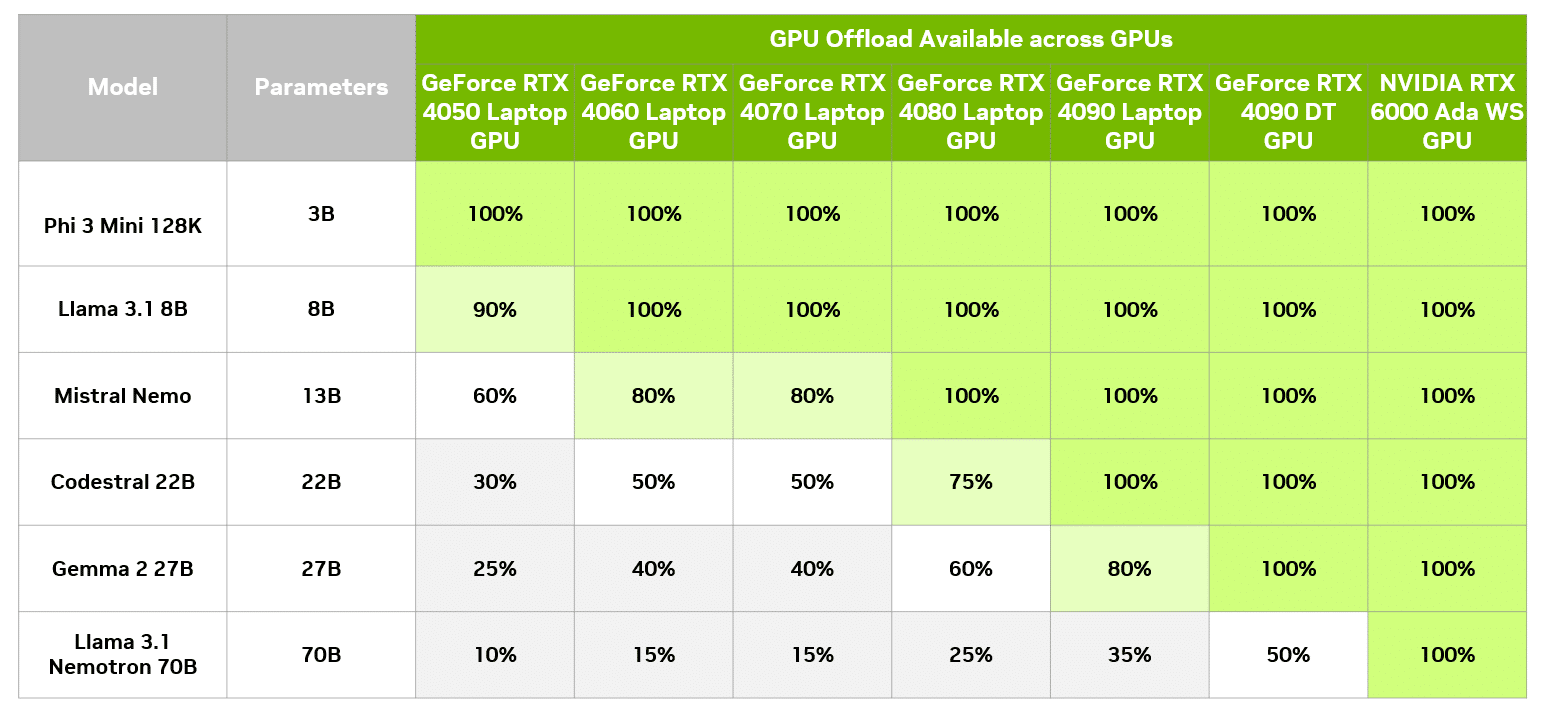
In LM Studio, it’s possible to assess the performance impact of different levels of GPU offloading, compared with CPU only. The below table shows the results of running the same query across different offloading levels on a GeForce RTX 4090 desktop GPU.
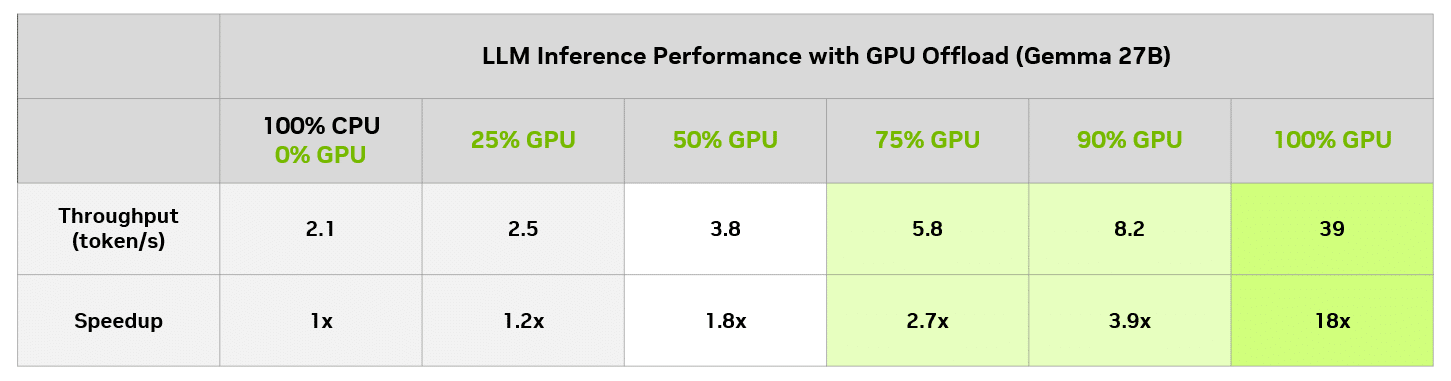
On this particular model, even users with an 8GB GPU can enjoy a meaningful speedup versus running only on CPUs. Of course, an 8GB GPU can always run a smaller model that fits entirely in GPU memory and get full GPU acceleration.
Achieving Optimal Balance
LM Studio’s GPU offloading feature is a powerful tool for unlocking the full potential of LLMs designed for the data center, like Gemma 2 27B, locally on RTX AI PCs. It makes larger, more complex models accessible across the entire lineup of PCs powered by GeForce RTX and NVIDIA RTX GPUs.
Download LM Studio to try GPU offloading on larger models, or experiment with a variety of RTX-accelerated LLMs running locally on RTX AI PCs and workstations.
Generative AI is transforming gaming, videoconferencing and interactive experiences of all kinds. Make sense of what’s new and what’s next by subscribing to the AI Decoded newsletter.