Whether they’re monitoring miniscule insects or delivering insights from satellites in space, NVIDIA-accelerated startups are making every day Earth Day.
Sustainable Futures, an initiative within the NVIDIA Inception program for cutting-edge startups, is supporting 750+ companies globally focused on agriculture, carbon capture, clean energy, climate and weather, environmental analysis, green computing, sustainable infrastructure and waste management.
This Earth Day, discover how five of these sustainability-focused startups are advancing their work with accelerated computing and the NVIDIA Earth-2 platform for climate tech.
Earth-2 features a suite of AI models that help simulate, visualize and deliver actionable insights about weather and climate.
Insect Farming Catches the AI Bug

Amid a changing climate, a key component of environmental resilience is food security: the ability to produce and provide enough food to meet the nutrition needs of all people. Edible insects, such as crickets and black soldier flies, are one solution that could reduce humans’ reliance on resource-intensive livestock farming for protein.
Bug Mars, a startup based in Ontario, Canada, supports insect protein production with AI tools that monitor variables including temperature, pests and number of insects — and predict issues and recommend actions based on that data. It can help insect farmers increase yield by 30%.
The company uses NVIDIA Jetson Orin Nano modules to accelerate its work, and recently announced it’s using synthetic data and digital twin technology to further advance its AI solutions for insect agriculture.
Seeing the Forest for the Trees
Based in Truckee, Calif., Vibrant Planet is modeling trillions of trees and other flammable vegetation such as shrublands and grasslands to help land managers, counties and fire districts across North America build wildfire and climate resilience.
NVIDIA hardware and software has helped Vibrant Planet develop transformer models for forest and ecosystem management and AI-enhanced operational planning.

The startup collects and analyzes data from lidar sensors, satellites and aircraft to train AI models that can map vegetation with high precision, estimate canopy height and detect characteristics of forest and vegetation areas such as carbon, water, biodiversity and built infrastructure. Customers can use this data to understand fire and drought hazards, and, with these insights, conduct scenario planning to forecast the effects of potential forest thinning, prescribed fire or other actions.
Delivering Tomorrow’s Forecast
Tomorrow.io, based in Boston, is a leading resilience platform that helps organizations adapt to increasing weather and climate volatility. Powered by next-generation space technology, advanced AI models and proprietary modeling capabilities, the startup enables businesses and governments to proactively mitigate risk, ensure operational resilience and drive critical decision-making.
The startup is developing weather forecasting AI and is launching its own satellites to collect environmental data to further train its models. It’s also conducting experiments using Earth-2 AI forecast models to determine the optimal configurations of satellites to improve weather-forecasting conditions.
One of Tomorrow.io’s projects is an initiative in Kenya with the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation that provides daily alerts to 6 million farmers with insights around when to water their crops, when to spray pesticides, when to harvest or when to change crops altogether due to changes in the local climate. The team hopes to scale up their user base to 100 million farmers in Africa by 2030.
Winds of Change
Palo Alto, Calif.-based WindBorne Systems is developing weather sensing balloons equipped with WeatherMesh, a state-of-the-art AI model for real-time global weather forecasts.
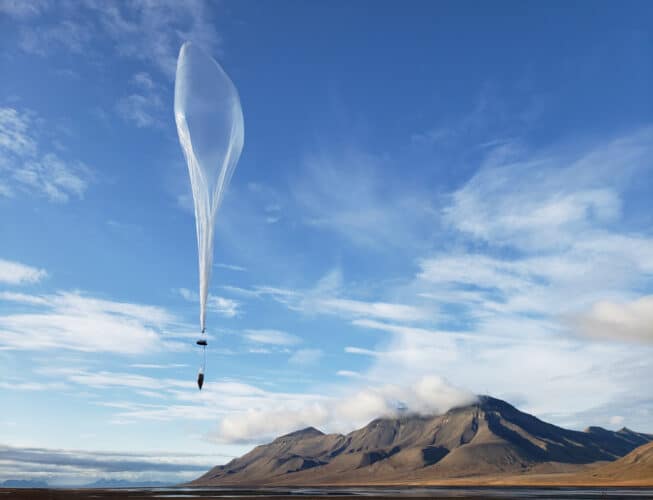

WeatherMesh predicts factors including surface temperature, pressure, winds, precipitation and radiation. The model has set world records for accuracy and is lightweight enough to run on a gaming laptop, unlike traditional models that run on supercomputers.
WindBorne uses NVIDIA GPUs to develop its AI and is an early-access user of Earth-2. The company’s weather balloon development is funded in part by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s Weather Program Office.
Taking the Temperature of Global Cities
FortyGuard, a startup founded in Abu Dhabi with headquarters in Miami, is developing a system to measure urban heat with AI models that present insights for public health officials, city planners, landscape architects and environmental engineers.

The company — an early-access user of the Earth-2 platform — aims for its temperature AI models to provide a more granular view into urban heat dynamics, providing data that can help industries and governments shape cooler and more livable cities.
FortyGuard’s technology, offered via application programming interfaces, could integrate with existing enterprise platforms to enable use cases including temperature-based route navigation, predictive enhanced EV performance and property insights.
To learn more about the Sustainable Futures program, watch the “AI Nations and Sustainable Futures Day” session from NVIDIA GTC.
NVIDIA is a member of the U.S. Department of State’s Coalition for Climate Entrepreneurship, which aims to address the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals using emerging technologies. Learn more in the GTC session, “Global Strategies: Startups, Venture Capital, and Climate Change Solutions.”
Video at top courtesy of Vibrant Planet.
