With the PyTorch 1.8 release, we are delighted to announce a new installation option for users of
PyTorch on the ROCm™ open software platform. An installable Python package is now hosted on
pytorch.org, along with instructions for local installation in the same simple, selectable format as
PyTorch packages for CPU-only configurations and other GPU platforms. PyTorch on ROCm includes full
capability for mixed-precision and large-scale training using AMD’s MIOpen & RCCL libraries. This
provides a new option for data scientists, researchers, students, and others in the community to get
started with accelerated PyTorch using AMD GPUs.
The ROCm Ecosystem
ROCm is AMD’s open source software platform for GPU-accelerated high performance computing and
machine learning. Since the original ROCm release in 2016, the ROCm platform has evolved to support
additional libraries and tools, a wider set of Linux® distributions, and a range of new GPUs. This includes
the AMD Instinct™ MI100, the first GPU based on AMD CDNA™ architecture.
The ROCm ecosystem has an established history of support for PyTorch, which was initially implemented
as a fork of the PyTorch project, and more recently through ROCm support in the upstream PyTorch
code. PyTorch users can install PyTorch for ROCm using AMD’s public PyTorch docker image, and can of
course build PyTorch for ROCm from source. With PyTorch 1.8, these existing installation options are
now complemented by the availability of an installable Python package.
The primary focus of ROCm has always been high performance computing at scale. The combined
capabilities of ROCm and AMD’s Instinct family of data center GPUs are particularly suited to the
challenges of HPC at data center scale. PyTorch is a natural fit for this environment, as HPC and ML
workflows become more intertwined.
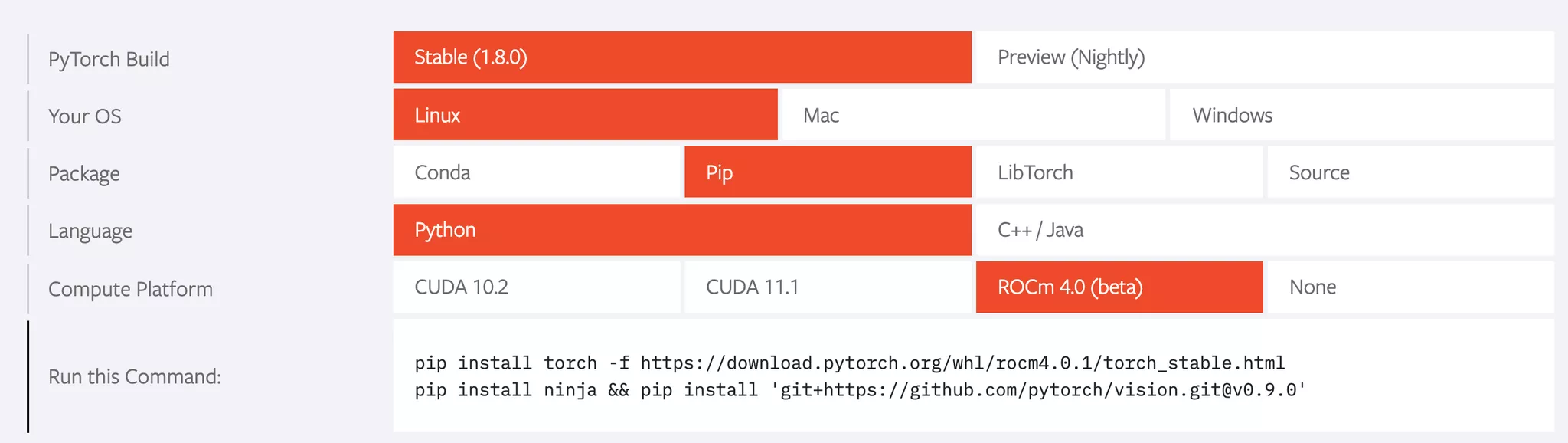
Getting started with PyTorch for ROCm
The scope for this build of PyTorch is AMD GPUs with ROCm support, running on Linux. The GPUs
supported by ROCm include all of AMD’s Instinct family of compute-focused data center GPUs, along
with some other select GPUs. A current list of supported GPUs can be found in the ROCm Github
repository. After confirming that the target system includes supported GPUs and the current 4.0.1
release of ROCm, installation of PyTorch follows the same simple Pip-based installation as any other
Python package. As with PyTorch builds for other platforms, the configurator at https://pytorch.org/getstarted/locally/ provides the specific command line to be run.
PyTorch for ROCm is built from the upstream PyTorch repository, and is a full featured implementation.
Notably, it includes support for distributed training across multiple GPUs and supports accelerated
mixed precision training.
More information
A list of ROCm supported GPUs and operating systems can be found at
https://github.com/RadeonOpenCompute/ROCm
General documentation on the ROCm platform is available at https://rocmdocs.amd.com/en/latest/
ROCm Learning Center at https://developer.amd.com/resources/rocm-resources/rocm-learning-center/ General information on AMD’s offerings for HPC and ML can be found at https://amd.com/hpc
Feedback
An engaged user base is a tremendously important part of the PyTorch ecosystem. We would be deeply
appreciative of feedback on the PyTorch for ROCm experience in the PyTorch discussion forum and, where appropriate, reporting any issues via Github.
